HTTP vs HTTPS: Why should I switch to HTTPS?
27th March 2017 • 5 min read
27th March 2017 • 5 min read

A common question for website owners is, “what is the difference between HTTP and HTTPS and how does it impact my website?” As a leading creative & digital agency, we understand the benefits of HTTPS from a security and trust perspective to SEO and data integrity.
This guide will answer common questions about HTTPS and how you can benefit from using it for your website.
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is the secure version of HTTP. It is the protocol over which data is sent between your web browser and the website to which you are connected. If a website is hosted on HTTPS and has a valid SSL certificate, all communications between your browser and the website are encrypted.
HTTPS is commonly used to protect confidential online transactions such as online banking or online purchases but it also has other benefits; meaning more and more websites are making the transition.
To use HTTPS, you will also need a valid SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate for your website.
There are multiple ways to check if a website is secure and has a valid SSL Certificate.
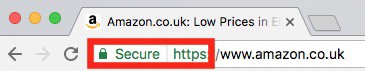
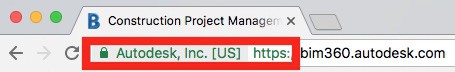
One way is to input the domain into an SSL checker. In most cases, the URL in your browser will also show either HTTPS if the site is secure, or a padlock symbol.
HTTPS can be shown in many ways across different browsers. Generally, you will see a green “secure” sign or padlock next to the URL in the address bar as seen below.
There are no negative impacts of changing your website from HTTP to HTTPS providing the transition is done correctly and seamlessly. For more information on executing, view Google’s guide on site moves and for Google’s guide on best practice when securing your site with HTTPS.
Follow these steps for how to change to HTTPS:
1. Buy an SSL Certificate – Free SSL certificates can be obtained via Let’s Encrypt. There are 3 primary types to choose from:
2. Install your SSL Certificate (more information on installation can be found here)
3. Update all hard-coded links to HTTPS
4. Update custom JS, Ajax libraries to HTTPS – Check domain for non-secure content using this online tool
5. Add 301 Redirects to new HTTPS URLs – Ensure this is done correctly to keep SEO benefits. Providing these are done correctly it will ensure that majority of existing SEO link equity is passed through
6. Update robots.txt file
7. Install SSL Certificate on CDN
8. Update origin URL on CDN
9. Enable HTTP/2 support on CDN
10. Update all hard-coded CDN links to HTTPS
11. Create new Google Search Console Profile, create and submit new sitemap
12. Update and resubmit your disavow file if you have one
13. Update Google Analytics profile URLs by navigating to the following locations:
If the process seems overwhelming and too difficult for you to execute, have no fear, we are here to help. Contact Torpedo with any website, digital or creative needs and leave the rest to us.